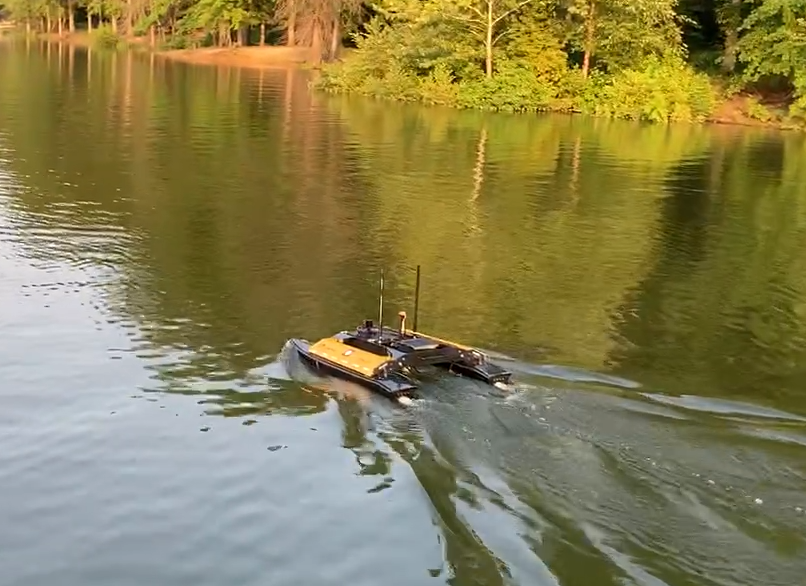

Robotic Information Gathering
Robots often need to learn an environment model in real-time, simultaneously gathering data to build and refine it.

Robots often need to learn an environment model in real-time, simultaneously gathering data to build and refine it.
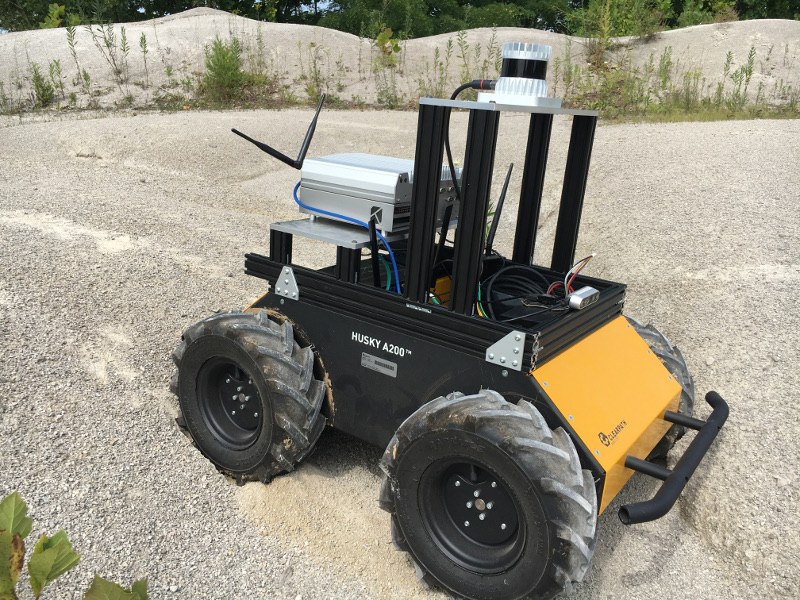

Consider the safety issue of navigating complex terrains like rocky fields, dense forests, or mixed-domain areas such as wetlands interspersed with vegetation.
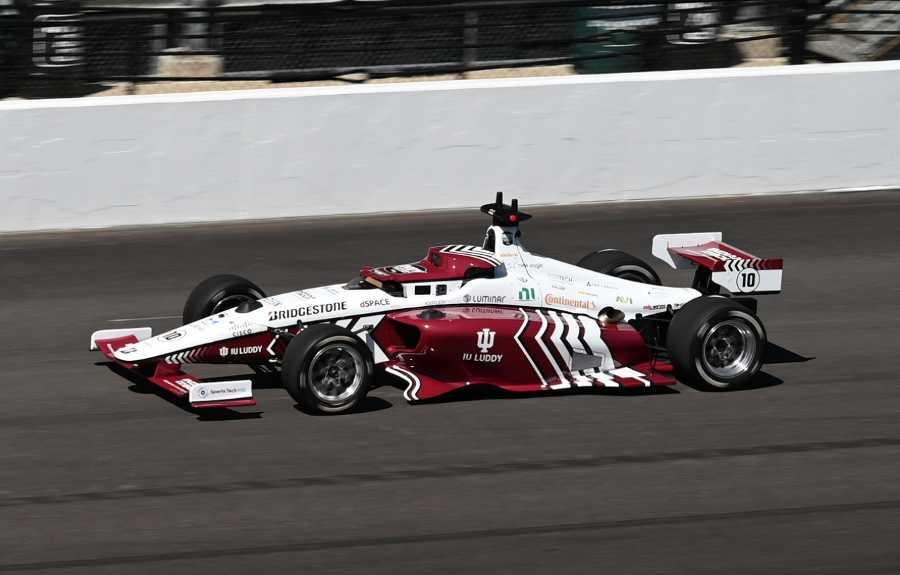

Autonomous racing introduces numerous challenges, especially when vehicles reach speeds exceeding 150 mph.
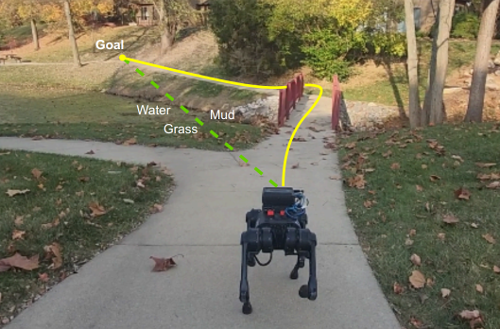
Identifying navigable space using onboard sensors is a fundamental capability for all robots,
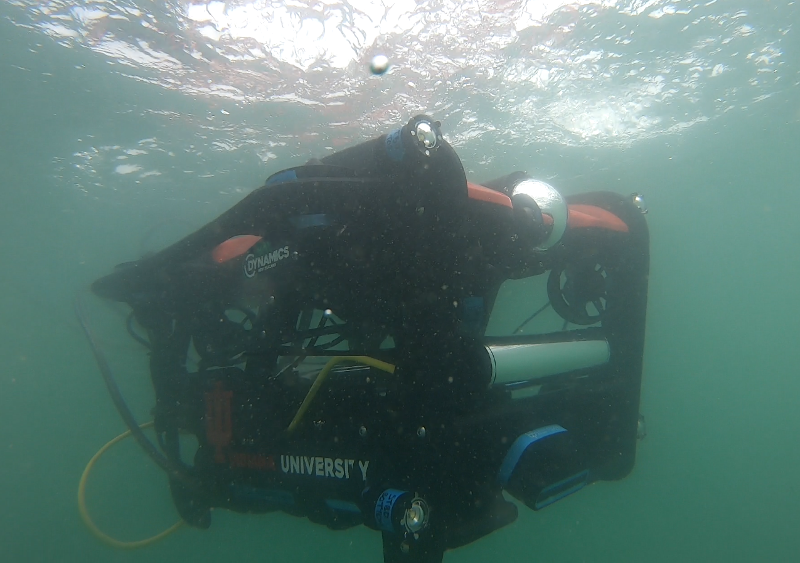
Robots must handle the inherent uncertainty of the world. This also relates to efficient reinforcement learning.
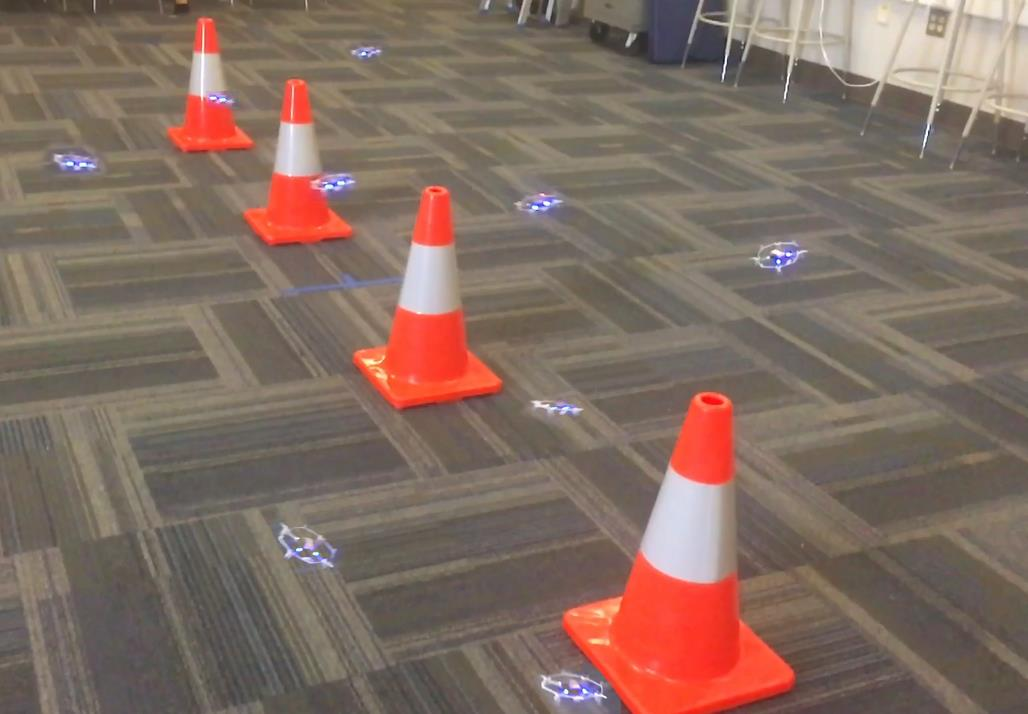

Many robots can collaborate to explore 3D spaces, interacting with each other, static obstacles, and dynamic objects like humans.
Copyright © 2018 - All Rights Reserved by VAIL
Template by OS Templates